Layout1
Check out my blog post from Blooloop on the design process and thinking behind my favorite little zoo that could:Big Bear Alpine Zoo. Take a look here.
My company is just me. And that’s by design. I do not intend to hire employees and I purposefully keep my fees and client volume low. I view it as a complete success, but given the common perception of “business success,” I often wonder if others would agree… In this article, I outline my business strategy of Growing Small as an alternate measure of success.
Believe it or not, many consultants, including yours truly, are actually introverts! Learn the best practices for working with introverts by reading Felis Consulting’s somewhat self-effacing and certainly vulnerable ‘Top Tips for Working with Introverted Consultants.’
As a designer dedicated to the long-term planning of zoos and aquariums, I’ve had to explain the process of master planning many times, and although every zoo and aquarium is different, the best master plans (i.e. those which have been implemented) always follow a similar structure. In this post, we address the most commonly asked questions to help you understand what master planning is, when is the right time to start, and who should be involved.
The city of Lafayette, Indiana has one of the oldest—and best—small zoos in the country. Recent renovations, thoughtful and modern designs, and focusing on providing for their local guests as top priority are a few reasons they are successful.
Zoos and aquariums have a long way to go related to being community assets that are truly reflective of their surrounding communities. Recent discussions in the AZA suggest that instead waiting for ‘best practice’ solutions, that individual organizations must start somewhere acknowledging that our strategies will evolve as we all learn the most productive ways to approach DEAI.

Layout1
Check out my blog post from Blooloop on the design process and thinking behind my favorite little zoo that could:Big Bear Alpine Zoo. Take a look here.
Adapted from 2015 AZA National Conference presentation "Brand and Experience: Communicating Conservation to Millennials and Gen Z"Zoos and aquariums are evolving. Conservation, once a secondary or tertiary goal of these institutions, has become a primary goal in recent decades—and ultimately, should become the singular, highest priority. Most American zoos and aquariums have been developing, leading, and supporting conservation efforts on their own properties and in situ to varying degrees for many years. However, with the creation and implementation of the AZA’s SAFE program, these institutions are making a concerted effort to unite as one powerful force for conservation. Prioritizing conservation above other zoological needs is a challenge, but perhaps more daunting is spreading awareness of this amazing work to the general public--changing the perception of zoos and aquariums from being “a place for a fun, family day out” to being “conservation organizations that also offer a fun experience.”
This challenge comes down to brand.
Brand is so much more than a logo. It is the perception that lives in your customer’s mind. It is the accumulation of the marketing messages you put out PLUS the experiences your customers have related to your organization. And these experiences are not limited to what they see or feel while on-site; it is also what they hear from their friends and family, what they read online, what they see on social media. The experience is the wildcard—the intangible that affects brand perception; the piece of the brand puzzle that we don’t truly own. But, we can influence experience by infusing brand into every aspect of the on-site experience. Because it is more difficult to control and more often overlooked by institutions, experience is the most important aspect of brand to address today at zoos and aquariums.

taco-bell-knows-their-target-market
Don’t believe me? Let’s take a look at a simple example of experience influencing brand: Taco Bell vs. Chipotle. Both restaurants offer similar products: fast Mexican. But we all clearly understand that there is a difference between the two. This comes down to how each differentiate based on a clear definition of and dedication to brand.

From AP Images
Taco Bell is a value brand, catering mostly to a young market (Generation Z & young Millennials) through efficiency, and vibrant, bold marketing.

chipotle (1)

Chipotle, on the other hand, differentiates based on quality—both in food and in guest experience. Chipotle espouses social and environmental responsibility through fresh, locally sourced ingredients and face-to-face interactions. Gone are drive-thrus and ordering from a disembodied voice in a nondescript box. Chipotle requires you to park your car, walk into the store, stand in line with other customers, order from an actual person, and has built its menu on the idea of customization. You get exactly what you want, from a real person, giving you real food that you can smell and see being cooked. And it’s done fast.
Chipotle knew that if they wanted to differentiate their brand from Taco Bell, they had to change everything—including the experience. They had to change the paradigm of tacos.
Today, Chipotle and Taco Bell are so different that Taco Bell doesn’t truly compete with Chipotle—despite having simila
r products. Taco Bell competes against similar experiences. They compete against the McDonald’s, Burger Kings, and Jack-in-the-Boxes of the world.
But how does this relate to zoos and aquariums?

From Conservationalliance.com
Let’s start with brand perception. As a whole, what do people think of zoos and aquariums today? Are they thought of in the same way as more traditional conservation organizations like World Wildlife Fund or Sierra Club? Perhaps more importantly, should they be striving for that association? Or, should they be differentiating themselves into a new brand that reflects who they are in a more meaningful way? They are different to begin with. They have animals that people can connect with in a deeply personal way. They have visitor experiences. They have tacos.
The question is: what kind of taco do you want to be? The Fun Taco? Or the Responsible Taco?
Today, zoos and aquariums are, by and large, Fun Tacos. They provide good family experiences. Wholesome days out. But, as Responsible Tacos, they’ll do that and more. They’ll provide real conservation impact through in situ programs AND opportunities for guests to get involved and get educated. They’ll make conservation education a key goal for ALL guests, not just for those who show extra interest.
In order to become Responsible Tacos (and be recognized as such), zoos and aquariums must change the paradigm of experience. You must realize that every moment your guest spends on-site is an opportunity to convey brand, tell stories, and educate. That every element of the physical incarnation of your organization reflects your brand’s perception. Because brand and brand perception is not JUST about your marketing message, but also inherently about experience.
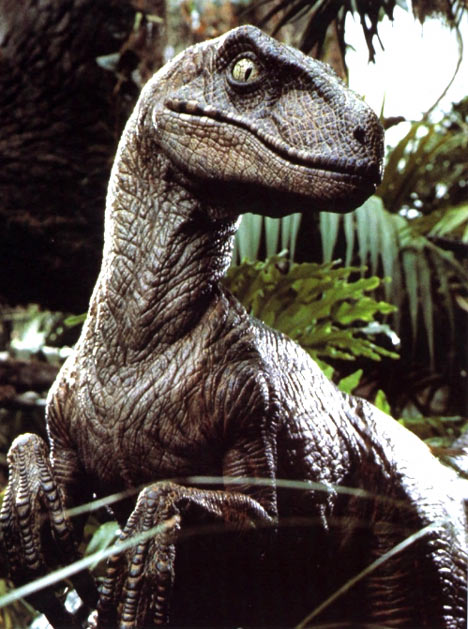 Check out my newest article, "What Jurassic World Teaches Us About Zoos," written with colleague Eileen Hill, for InPark Magazine. InPark has an historically theme park centered readership, and this article focuses on how attractions across the spectrum are learning from each other. Also, dinosaurs!!
Check out my newest article, "What Jurassic World Teaches Us About Zoos," written with colleague Eileen Hill, for InPark Magazine. InPark has an historically theme park centered readership, and this article focuses on how attractions across the spectrum are learning from each other. Also, dinosaurs!!
 February's addition is near and dear to my heart as it's the PGAV-designed Sea Lion Sound at Saint Louis Zoo. This exhibit won a Significant Achievement Award from the AZA, and features both an underwater viewing tunnel and an immersive theater. Check it out--here!
February's addition is near and dear to my heart as it's the PGAV-designed Sea Lion Sound at Saint Louis Zoo. This exhibit won a Significant Achievement Award from the AZA, and features both an underwater viewing tunnel and an immersive theater. Check it out--here!
 About 20 years ago, the zoological society that oversaw the system of zoological facilities in and around the New York metropolitan area underwent a brand facelift. They became the Wildlife Conservation Society—a deep integration of the five metro facilities with the conservation organization that had existed since the late 19th century. And, as I’m sure they would argue, it was much deeper than simply brand: it was a laser sharp focus on mission. Specifically, the mission of conservation.
About 20 years ago, the zoological society that oversaw the system of zoological facilities in and around the New York metropolitan area underwent a brand facelift. They became the Wildlife Conservation Society—a deep integration of the five metro facilities with the conservation organization that had existed since the late 19th century. And, as I’m sure they would argue, it was much deeper than simply brand: it was a laser sharp focus on mission. Specifically, the mission of conservation.
The discussion of zoos as conservation organizations is admittedly a quagmire: zoos and aquariums are no doubt contributing to the conservation of species. The degree to which they are contributing depends on the individual institution, and the public perception of them as conservation institutions is probably as convoluted. But this post is not about zoos as conservation organizations. This is about conveying that message to your public. This post really is essentially about brand.
Last year, I had the pleasure of spending a late summer weekend with a colleague exploring three of the WCS facilities: Central Park Zoo, Bronx Zoo, and New York Aquarium. Each are as unique from each other as snowflakes: Central Park Zoo is a delightful historic gem tucked into a city park where wealthy urbanites can escape their apartments for an hour with their children. The Bronx Zoo is a massive, day-long excursion winding through mature forest—as much a nature experience as a zoo. The New York Aquarium, still recovering from storm Sandy, is a small to medium sized aquarium on par with any found in a medium-sized city—think Landry’s, SEA LIFE, Ripley’s.
However, each clearly conveyed the WCS message: We are conservation.
The sea lion show at the Aquarium. The Madagascar (and of course the Congo) exhibit at Bronx. The Rainforest exhibit at Central Park. Each clearly stated and restated the conservation issue, the solution, and how WCS is involved. This is done through graphics, video, docents, and message-driven immersive storyline. The exhibits are beautiful. Each thoughtful, innovative, and clearly immersive. Each exhibit created with upmost care by a talented team of designers who obviously has the formula down to a science. These places are conservation. You cannot miss it.
This prototype of zoo as conservation organization is a clear success story and model for other zoos as we continue to showcase the amazing work zoos and aquariums do every day—and too often behind the scenes. As we continue to evolve this model, a particular emphasis should be focused on further blending conservation education and fun. While WCS is successfully integrating conservation into the experience, it does, at times, feel a bit heavy-handed—overwhelming guests with bad news and bleak outlooks for the future. People come to our institutions for wholesome family fun, and the integral blend of pure joy, amazement, and conservation education will be the foundation of successful zoos and aquariums of the future.

Fantastic campaign. I encourage all bloggers to join up and everyone else to donate. Thanks for bringing this campaign to my attention, Lady of the Zoos!
by Jon Coe Greetings zoo friends and thoughtful critics!
If you have fifteen minutes have a look at the video below. This is the complete elephant show from Bali Safari & Marine Park, and my long time friends and client, Taman Safari Indonesia. [youtube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-cNml7-KUTQ] I designed the elephant show venue, including the wrap around water feature with underwater elephant viewing. But the important thing is how this show has evolved from a somewhat circus-like show demonstrating human control over elephants to a conservation melodrama where elephants are characters in the play, often performing well out of sight of trainers.
The drama starts from the expected view of forest cutters and loggers as “bad guys” (dressed in black as in traditional Asian drama) harassing, shooting, “wounding” and driving off elephant “victims”. But in the next scene the elephants become “bad guys” destroying village crops and endangering local people. Finally elephants, under proper Forestry Department management, become heroes and win local support.
To me these abrupt and startling changes of perspective are effectively used to suggest the real complexity of wildlife conservation. The show mentions Taman Safari’s long-term support of the Way Kambas National Park elephant sanctuary they developed in Sumatra with the Forestry Department. But it is careful not to propose unrealistic “quick fixes” or blame either villagers or elephants. It presents, albeit in cartoon style, the realistic certainty that hard choices and compromises are required to create sustaining populations of farmers and elephants. The final message is something like “We don’t know the answer, but we know we will find the answer by working together”. Who can argue with that?
On a practical level, I’m not a supporter of full contact elephant management or coercive training methods. But in this case, however training is done (and I don’t know how it was done) a number of elephants individually and collectively carry out long sequences of learned behaviours far from trainers. And while some appear to be “going through the motions”, others are clearly having fun. Most trainers would not encourage training elephants to chase people, even on stage. But the young elephants do seem to enjoy this part...wonder why!
From a behavioural enrichment perspective, the elephants have a wide range of physical activities including short bursts of running and swimming in a highly varied pace, usually with conspecifics. While the routine isn’t varied, neither is the exercise routine of most human athletes and performers, who nevertheless seem to find them enriching.
Most guests wouldn’t recognize the high levels of training skill and innovation required to produce such a show. They, especially high numbers of children, simply want to be entertained in enjoyable and understandable ways. In my experience such shows are the best way to connect with large audiences in mass tourism settings, where individualistic immersion on simulations of isolated jungle trails fail. In my opinion, major zoos can and should have both to reach their highly varied audiences most effectively and create that moment of “positive arousal”, as Terry Maple refers to it--that bonding moment of empathy upon which all effective education is based.
Jon Coe is a world-renowned zoo designer with over one hundred and sixty planning and design projects for over eighty-two zoos, aquariums, botanical gardens, theme parks and national parks in thirteen nations. The goal of his work is to collaborate in the creation of enriching and sustainable environments for people, plants and animals.
I was recently interviewed for an article about the complexities of zoo design especially in relation to animals' needs. It's a great article on VetStreet.com. Check it out!
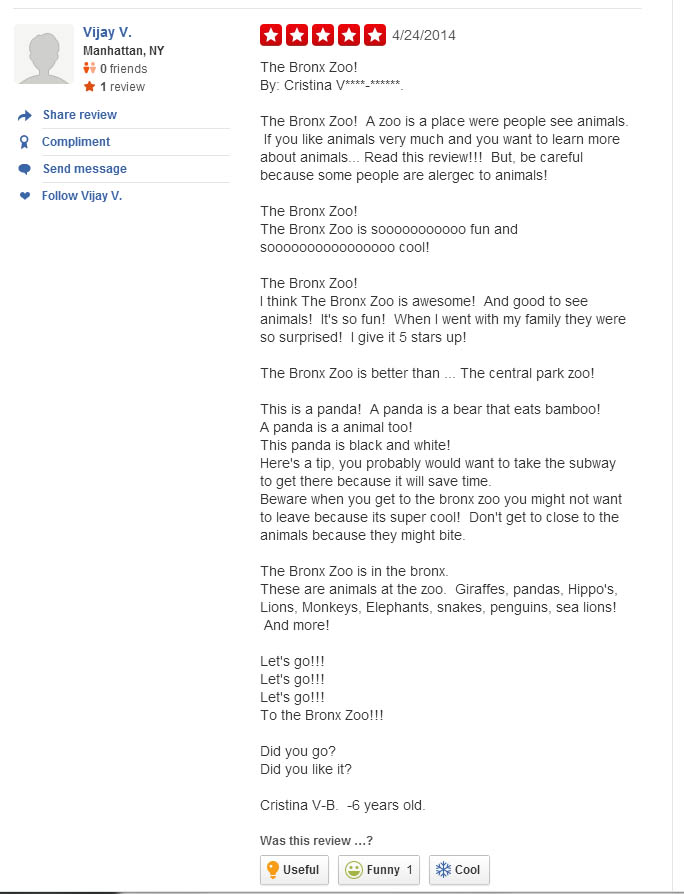
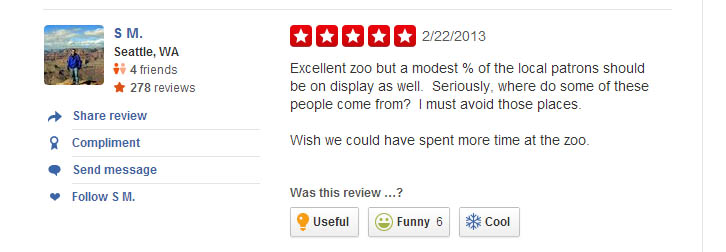
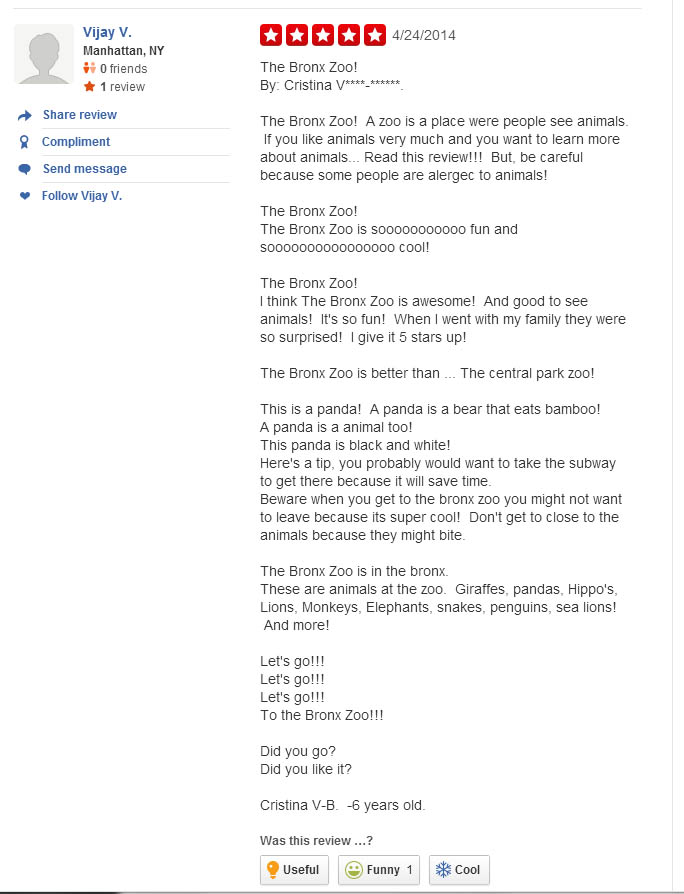
Reputation is everything. We’ve known this since middle school. That’s why it’s important to carefully monitor your public perception, especially if you are an institution supported primarily through admissions and tax support. With the instant feedback available 24-7 on internet review websites, there is simply no excuse for any zoo or aquarium to not be aware of public sentiment. Interested in what the general populace was thinking and inspired by my favorite podcast, How Did This Get Made?’s “Second Opinion” segment, I wandered the lonely streets of Yelp.com to find the best 5 Star Reviews of “top 5” Zoos around the country. What I uncovered was by and large disappointing: well-conceived, coherent, thoughtful reviews of zoos that are deeply cherished by unwavering, supporting communities.
But then there were these.
San Diego Zoo
St. Louis Zoo

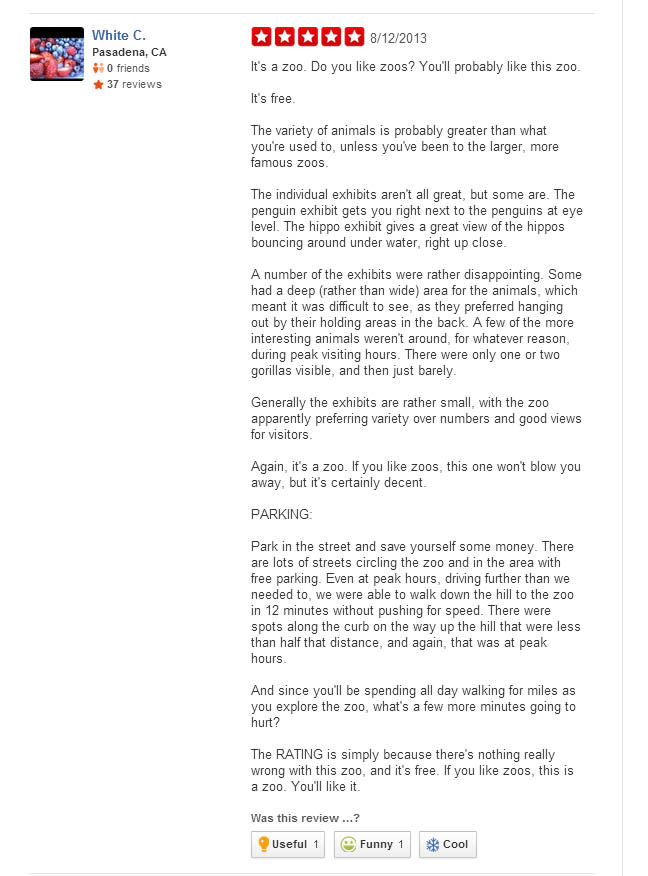


Henry Doorly Zoo



Columbus Zoo

Bronx Zoo

Each week, I receive at least one email from an enthusiastic young soul asking for advice on how to become a zoo designer. Many requests are from college students, already several years into design school. Others are from enterprising high schoolers (and a junior high schooler or two) planning their futures. I've even corresponded with several mid-career adults, looking for guidance on how to change career paths. Every one of them (and, I assume, you, too!) are passionate about animals and seek to share that passion with zoo guests--to help them create connections to wildlife and become advocates for our natural resources. That's very admirable. That's where I started (and what keeps me energized), too.
But, let's talk some realities. As a zoo (and / or aquarium) designer, you will likely work for a private design firm, not a zoo. Zoos these days are starting to understand the value of on-staff designers, but the reality is, very few zoos actually have them; and more often than not, they do very little actual design work, or are relegated to small projects such as signage, snack stands, or demonstration gardens, leaving major capital projects to licensed architectural firms with greater resources. These zoo positions are usually most valuable as client representatives during the design and construction phases, acting as go-betweens (and sometimes decision-makers) for the zoo administration when communicating to designers and contractors. I do believe we will see an increase in these types of positions becoming available, though, as institutions realize the value of having staff that truly understand and are highly literate in design and construction--they can provide great insight to their consultants about the zoo itself, local regulations, and increase the efficiency of communication between consultants and staff, not to mention the fact that they understand drawings and help prevent issues down the line thus ultimately saving the zoo money.
So, let's say you're ready to get a job with a firm. Where do you start? Within the U.S., three major firms specialize in zoo and aquarium design (depending on how you define 'major'), and are generally the three competing for the major projects: Portico Group is in Seattle; PGAV Destinations is in St. Louis; CLR is in Philadelphia. Beyond these three, there are about 10+ small and medium firms, ranging from <5 staff to about 30 staff, located around the country that have completed zoo / aquarium design work, or specifically specialize in such. Seattle is a hot bed of activity due to "patient zero" Jones & Jones, from which most, but not all, firms that specialize in zoo design spawned. Wichita, New Orleans, and Boston are home to several others. If you decide you want to be a zoo or aquarium designer, you will likely live in one of these cities. I hope that's okay.
You've gotten a job! Congratulations! You've moved in, you're ready to go. Now what's the day to day for a zoo designer? Likely the first few years will be painful. Trust me. It's not what you expect. You'll have long hours (50-60+ hour weeks regularly) staring into the abyss of the computer, drawing things that someone else designed. Figuring out the details like the hinge on a gate or how to downspout a thematic wall. You likely will not do site visits or even be able to meet the clients for several years, until you've proven your worth. You may be shuffled from one project to the next without seeing a project from start to finish, often juggling multiple projects at once. But, it does get better, although not much more glamorous! When you do finally reach the point in your career when you get to visit the zoo you're working singularly for, you generally only get to see the inside of a conference room on a quick one or two day trip--where you'll spend the evening working in your hotel room on drawings that you didn't get to complete because you spent the whole day inside that conference room.
Still interested? Yes? Okay--let's get to what you really want to know: How do you become a zoo designer?
I wish there was a magic answer to this. There is no school of zoo design. No specific university, no highly specialized curriculum. Right now, if you want to become a zoo designer, you have to do it of your own accord. Most of today's successful zoo and aquarium designers fell into their jobs. They may have done a college project or volunteered at their local zoo, but the vast majority became zoo designers by dumb luck. They were architects or landscape architects that happened to work at a firm that happened to get a zoo project, and over time, one project became many. Before they knew it, they were experts. But, the fact that I get so many inquiries is telling me this is slowly changing. As zoos evolve, and exhibits become more engaging, young people are realizing the potential for design careers focused entirely on zoos and aquariums (museums and theme parks, too!). This will lead to more and more students with specialized experiences and focused educations. So how will you stand out??
Here are the basics I recommend:
Two degrees: Architecture or Landscape Architecture AND Zoology / Biology / Animal Sciences. It does not matter which design field you choose. The majority of the early design firms specializing in zoo design were traditionally landscape architects. That has changed. Architecture and landscape architecture are inextricably integrated when it comes to zoo design. Of course, if you are more inclined to design for aquariums, choose architecture. But if you want to design only for zoos or for both zoos and aquariums, go with what is more appealing to you. Do you like to design structures? Or are outdoor environments more appealing to you? Go with what will be most interesting to you. As for the science degree, this is not required, but is very appealing to employers. This will set you apart from other design-only students. You could also just get a minor, but doing so will be very challenging, as zoology is a highly rigorous degree while design school is extremely time-consuming. It is possible, but it will not be fun.
Focus every project where you have a choice of topic on zoos or aquariums. Believe me, it will be a challenge. You will get a lot of push-back from design profs wanting to encourage you to expand and explore. Go ahead, but if you truly believe you want to design zoos, you'll want every opportunity possible to explore this complex field.
Get an internship at a zoo / aquarium. Doing anything. You don't have to have a design internship. Repeat. You do not need a design internship at a zoo. You do need behind-the-scenes experience. Do an animal care internship. Do a marketing internship. Do whatever kind of internship you can get. You will need to understand every aspect of zoos in order to design effectively for them.
Get an internship at a ZOO / AQUARIUM design firm. Do not just get an internship at the local architecture firm near your university. This is a chance to see how zoo design really works, and get your foot in the door to one of the very few specialist firms in the country. While you are there, work hard. Ask lots of questions. Share your passion. We remember it when it comes time for you to send in your resume after all those years of school.
Research and network on your own. Visit zoos and aquariums as often as possible, attend AZA conferences, visit zoo design firms, get to know designers, get to know your local zoo. Basically, ask loads of questions, read as much on the topic as possible, get tours and behind the scenes as often as possible. Learning on this topic is not going to happen in school. You have to spend your own personal time researching and educating yourself.
One of the wonderful things about the zoo and aquarium industry is that most people involved are kind and willing to help, if you ask. Zoo and aquarium personnel are in it for
the love of animals, and usually are more than happy to answer questions or direct you to someone who can. I had a lot of great people help me get to where I am today, and hopefully, I can repay their kindness by helping others on their own journey. As always, if you have any questions or need advice, just ask.
If you'd like another zoo designer's opinion, check out Jon Coe's paper on how to become a zoo designer. There is definitely much overlap!
Good luck!!
by Ben Cober
 Recently I really enjoyed Bryan Wawzenek’s Theme Park Insider post about the top ten songs about theme parks. I started to plunge into the depths of the internet to seek out the best jams about our beloved zoos, and was shocked to find out that there currently exists no central repository for tunes on this great topic!
Recently I really enjoyed Bryan Wawzenek’s Theme Park Insider post about the top ten songs about theme parks. I started to plunge into the depths of the internet to seek out the best jams about our beloved zoos, and was shocked to find out that there currently exists no central repository for tunes on this great topic!
Therefore, as we celebrate the opening of Heart of Africa at the Columbus Zoo and Aquarium and the beginning of zoo season, I present the Top 10 Songs about Zoos. These have been pulled from some of the darkest corners of discussion forums and web obscurity, so most might not bring on the waves of nostalgia that Freddy Cannon’s Palisades Park might, but are still a great journey through artists’ love of these great destinations.
At the Zoo Simon and Garfunkel Single (1967)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6xKLBne1CoI
At the Zoo is a tribute by Paul Simon to his hometown of New York City. While it chronicles Simon’s trip to the Central Park Zoo, the song was later licensed in advertisements to the Bronx and San Francisco Zoos in the 1970s. The song hit #16 on the Billboard Hot 100 when it was released and its lyrics were adapted by Paul Simon in 1991 into a children’s book.
Going to the Zoo Peter, Paul, and Mary Peter, Paul, and Mommy (1969)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vhxttDEv_I8
Going to the Zoo was released on side two (you read that right, remember when albums had SIDES?!) on Peter, Paul and Mommy by Warner Brothers. It was the group’s first children’s album, and took home a Grammy the following year for the Best Album for Children.
Zoo Song Alison Steadman and Roger Sloman Nuts in May (1967)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=daEocG2dKCU
Nuts in May was a comedy movie for TV that was broadcast on the BBC in the late 1970s. The movie follows a nature-loving, self-righteous couple trying to enjoy their idyllic camping holiday. A nearby camper comes to check out their campsite, and is reluctantly treated to a song the couple “made up last year” about their trip to a zoo in London. The banjo and guitar skills are….questionable, and the lyrics are rather…uninspired, increasing the awkward tension between the poor guest and the couple.
Perfect Day Lou Reed Transformer (1972)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QYEC4TZsy-Y
If you do a little research, this song gets deep. While not solely about the zoo, Perfect Day is thought to allude to Reed spending a day in Central Park with his first wife, Bettye Kronstad, that includes “feed animals in the zoo.” The song was produced by David Bowie and Mick Ronson, and was featured in 1996’s Trainspotting; a 1997 BBC charity single which made it the UK’s number one single for three weeks; an AT&T commercial during the 2010 Olympics; and commercials for the PlayStation 4 and Downton Abbey. {Editor Note: This is my favorite. Stacey}
Funky Gibbon The Goodies Single (1975)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iAmx_XdQky8
The Goodies were a comedy trio in the 1970s and 1980s that released a number of humorous tracks, Funky Gibbon among them. The song is an “instructional video” that teaches a dance the group made up about their favorite primate while they were at the zoo. It was their most successful single, and entered the UK singles chart at #37 in the spring of 1975. Slightly awkwardly, in the “About” section on the above clip, one of The Goodies shows' biggest claims to fame was that it was so funny that it actually killed a man from King’s Lynn by making him laugh himself to death. Ok…
Sonntags im Zoo (“Sundays at the Zoo,” translated from German) Die Toten Hosen (“The Dead Pants” – Google Translate, don’t ask) Unsterblich (“Immortal”) (1999)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J8WHZjhWzLY
Despite the rough, punk-rock sound of this German thrash, the song is actually about a really nice day at the zoo and loving all the different animals. Don’t believe me? First verse: “Look at the giraffes, their necks are long. Look how they smile, they say thank you.” The chorus? “Here we are happy – you and I. Here we are free – on a Sunday at the zoo.”
The band is originally from Dusseldorf, their name colloquially meaning “The Dead Beats.” Amazingly, this album is considered as one of their more “peaceful and quiet” ones, and the band apparently hated the album cover – a filtered photo of the Alps with pine trees and a sign reading “until we meet again!” Sounds pretty punk, anti-establishment to me!
5 Years’ Time Noah and the Whale Single (2007)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y3PELIU1i4c
Once again, similar to Lou Reed’s Perfect Day, 5 Years’ Time isn’t really directly about a zoo, but more about a couple imagining what their relationship will be like in five years – as they walk around the zoo. (That’s a nice sentiment, right? A couple’s dream spot in the future is a zoo!)
Sadly the song didn’t do too well when it was first released; but when the group re-released it in August of 2008, it became the group’s first top-ten hit, climbing to number 7 on the UK charts. The music video kind of feels like a Wes Anderson film, and was featured in a 2008 SunChips commercial.
The Carnival of the Animals Camille Saint-Saëns Composed 1886
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wBGEf4urGNo
So this gets really interesting. Carnival is a musical suite comprised of fourteen movements by French Romantic composer Camille Saint-Saëns, which follows a jaunt through the zoo and the different animals met along the way. It’s a rather comical piece, based on earlier works it references in more playful manners.
Saint-Saëns actually didn’t want Carnival published until after he had died, since he had written it “for fun” and was worried it would detract from his more serious, professional works. Little did he know that it would go on to become one of his best-known works. Covers of the various movements can be found in Fantasia 2000, Space Mountain, a trailer for The Godfather Part II, Babe, Charlotte’s Web, The Curious Case of Benjamin Button, The Simpsons, The Ren and Stimpy Show, How I Met Your Mother, France at Epcot, the famous piano duel between Bugs Bunny and Daffy Duck, during red carpet premieres at the Cannes Film Festival, and even Weird Al Yankovic did a cover called Carnival of the Animals, part II.
Daddy’s Taking Us to the Zoo Tomorrow Sung by Patsy Biscoe Sings Favorite Children’s Songs (1993)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ViW47oCeOlg
If Funky Gibbon by The Goodies can make the list, so can DTUttZT by Patsy Biscoe. The song is a pretty straight-forward children’s tune about going to the zoo, although sadly hasn’t achieved the notoriety or reach that many of the other songs on the list have.
Biscoe herself though is pretty fascinating. She was born in Shimla, India, and moved to Australia with her family after the Partition of India (which is basically when the Punjab and Bengal provinces were divided along with a number of assets). She studied medicine at the University of Tasmania, singing and playing music at a local jazz club on Sunday nights, and was a finalist on the Starflight International talent quest on Australian Bandstand. She was really popular on the local Adelaide children’s shows Here’s Humphrey and Channel Niners; and has been Deputy Mayor of the Barossa Council local government and a naturopath (which is a form of alternative medicine that says special energy called “vital energy” or “vital force” guides bodily processes).
Walking in the Zoo Alfred Vance Live (1870)
The internet refuses to relinquish the actual music, but here are the lyrics.
Vance’s real name was Alfred Peek Stevens, being that “Alfred Vance” was a stage name he used throughout English music halls in the mid-1800s. Walking in the Zoo chronicles Vance’s day at Regents Park’s Zoological Gardens in London with a lady, ending with a horrific mauling by a cockatoo. The song has two fascinating precedents set within it. First, it’s the earliest known use in the UK of the term “O.K.” in the sense that we actually think about it today – something being all right or good. Second, it’s also one of the earliest uses of the term “zoo” instead of “zoological garden” – which actually really upset some stuffier “zoological garden” professionals of the era.
Sumatran Tiger (aka Endangered Song) Portugal the Man Smithosonian's National Zoo (2014)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FoiIBYcRWKw
From National Zoo: "There are only 400 Sumatran tigers left in the wild. That's why the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute partnered with indie rock band Portugal. The Man, bringing science and music together to distribute a previously unreleased song titled "Sumatran Tiger." The song was lathe-cut onto 400 custom poly-carbonate records designed to degrade after a certain amount of plays. There are no other copies of the song in existence. The records were sent to 400 participants asked to digitize and share the song through their social channels with the hashtag #EndangeredSong. The song will go extinct unless it's digitally reproduced. The Sumatran tiger will go extinct unless we take action.
So what can you do? We need your help to share our message and raise awareness about the critically endangered Sumatran tiger and need for conservation efforts.
Scour the internet and search for the song using the #EndangeredSong on sites like SoundCloud, Radio Reddit, MySpace, Twitter and Facebook.
Retweet, repost and tell everyone you know. Visit www.endangeredsong.si.edu to learn more about the initiative and how to help perpetuate the song.
Conservation is a multigenerational issue that needs a multigenerational solution. We must reach and inspire the next generation of conservationists."
All sorts of great tunes! Feel free to make that playlist and sing along on the commute to your zoo!
Updated October 1, 2015:
I'm overjoyed to announce our project has received Top Honors in Exhibit Design from the AZA! I was lucky enough to watch CZA President and CEO accept the award at the annual awards luncheon at the National AZA Conference 2015 in Salt Lake City. Absolutely one of the great moments of my life so far...
It might surprise you to hear that I’ve been working at PGAV for 11 years now, and I’ve only seen a few projects that I worked on open. That’s something you may not know about being a designer (it’s kind of the industry dirty little secret); many projects that you dedicate years of work to, get shelved. Even with a high industry success rate, like what PGAV has, many projects disintegrate and disappear entirely.
Even with a high industry success rate, like what PGAV has, many projects disintegrate and disappear entirely.
What’s perhaps more interesting than that is that my role specifically at PGAV is generally focused on the largest scale planning—master plans for zoos and aquariums, conceptual storylines and site planning, exhibit programming and initial layout—which means my involvement in projects quickly tapers as more and more detail develops. For example, although I understand how to put together a swing gate in a wood fence, there are highly talented architects in our office who more thoroughly understand the exact finish, gauge, hardware, species of wood, width of gaps, and hinge detailing, and draw them quicker and more efficiently than I. These people pick up where I drop off, and they continue to see the project through to construction. Because of this, I often am not involved as projects develop past initial or conceptual planning. But, Columbus Zoo’s Heart of Africa is different. My involvement in this project continued, to one extent or another, from the master plan development through construction documents. This is truly the first project that I was so deeply involved in that actually made it to opening day. And I’m excited.
I got to visit Heart of Africa (originally called ‘Safari Africa’) on opening weekend which happened to fall on Memorial Day. My visit fortuitously coincided with what will likely be one of the biggest weekends the exhibit will ever see. I was nervous about this, but happy to say, despite the massive crowds, the exhibit worked. I even overheard probably the best compliment possible from a mom visiting a zoo: “That was so worth the crowd!” Amazing.
Let me tell you a little about the project. It’s a 43-acre expansion of the original zoo onto land that was previously used for farming. The expansion area, located to the northwest, provided an awkward connection point, and an even longer walk from the front door than already existed. Because of this, the project includes a new tram system connecting guests from the front door of the zoo to the front door of the exhibit.
Guests arrive to Heart of Africa through a massive entry gate, demarking the outskirts of the modern day African village built up around the front gate to an East African National Park. The village grew over time, as more and more tourists visited the Park, and its mixture of cultural influences are obvious in the architecture and murals found throughout. Just inside the village fence, (thematically) travelers are encouraged to leave their camels for rest in the corral. Hints of the villagers’ daily life dot the path into the heart of the village. The village itself contains the restaurant (with views to both the lions and savanna, as well as the camel ride paths), snack stand, ticket and photo stand, retail shop, and amphitheater. But the real attractions here are the lions and the view beyond—to the 8-acre savanna.
The lion exhibit extends from the village around past the National Park entry gates. Just within the entry gates, the Rangers’ work station and airplane hangar sit. The lions often are found here, lounging in the shade which happens to be surrounded by windows. You won’t get any closer than this. In the hangar, a transport plane encourages lions and children to explore, and if you’re lucky, you’ll get an unexpected face-to-face.
Past the lions, the savanna unfolds fully. In the middle of the savanna and closest to the guest path, the watering hole exhibit allows keepers to rotate education and exhibit animals throughout the day. Currently, the rotation occurs just about hourly. While I was there, a group of zebra and antelope inhabited the yard as I entered; on my exit, a flock of flamingos. This really got people talking which, ultimately, is the whole purpose.
The watering hole is also where the cheetah run demonstration occurs, providing a wholly different experience than seen at other zoos. This exhibit allows for a looping run, rather than just a straight run, and the keepers can easily change the run route to keep the exercise fun and enriching for the cats.
The cheetahs also have a permanent exhibit area highlighting the wonderful conservation program, Cheetah Conservation Fund, which the Zoo supports through funding. The exhibit area is basically an outdoor yard for the cheetahs, who are all used in education programming around the country. This means they have been hand-raised and bonded with keepers and litter mate Labradors to ensure they are tractable.
The savanna also includes a specialized giraffe feeding yard. This area allows the keepers to keep track of which animals have participated in the timed feedings—meaning, everyone remains on their appropriate diet. The feeding platform gets guests out into the savanna, providing an unimpeded view of the seemingly unending (meaning, no barriers anywhere!) savanna. Even when feeding is not occurring, the platform is open for viewing, and guess what--the giraffes like to hang out right there for up-close views.
Past the giraffes is Jack Hanna’s tented camp. Here you can explore a Jeep that has seen better days (as witnessed by the car parts nearby), and two tents filled with Jack’s supplies. One tent and campsite has been overrun by vervet monkeys—an authentic African experience (for those of us who have been to Africa)! The monkeys’ exhibit is filled with climbing structures and camping accoutrements. Keepers are able to scatter treats as enrichment throughout the space to keep the critters active. While I was visiting, the monkeys seemed to really enjoy sitting on the camp table and playing ‘paddy cake’ with the guests through the glass.
Overall, the exhibit has turned out just beautifully. So many of the original intentions and ideas are spot on. So much so, you can even compare the original renderings to site photos and clearly see how they align. It’s not often this so cleanly occurs without significant changes. It is a testament to the relationship between the Zoo and PGAV, and the Zoo’s clear vision, experience with large scale projects, and drive to achieve such a high level of success. Well done, team!
 Our friends over at ZooLex.org have invited DesigningZoos to partner with them to provide a place for readers to share their experiences and commentary on the new exhibit gallery additions. Every month, we'll post links to the new Zoolex exhibits here, and encourage discussion amongst readers in the comments section.
This Month: Beehive at Tiergarten Schonbrunn
Our friends over at ZooLex.org have invited DesigningZoos to partner with them to provide a place for readers to share their experiences and commentary on the new exhibit gallery additions. Every month, we'll post links to the new Zoolex exhibits here, and encourage discussion amongst readers in the comments section.
This Month: Beehive at Tiergarten Schonbrunn
"Beehive is an animal exhibit at the Vienna Zoo that challenges many stereotypes about zoo animals. The bees are free ranging, but not wild. They are domesticated, but not tame. They are scary for many people, but not dangerous. They are hardly noticed by most, but heavily needed by all. Beehive is a colourful and playful stage for their show."
Have you been to this exhibit? What do you think of it? Let us know, below!

By Eileen Hill
Click the link below to see Eileen’s slide show, along with her notes per slide.
Future of zoos_hill_with_notes_compressed_20140305
(Slide 2) I’m going to start with a brief overview on the evolution of zoos, and how I think this evolution will play out in the future. I have focused primarily on what future zoos are going to look like, what some of the new types of zoos will be, and how these different types of zoos will blur the boundaries with other institutions. That’s what I’m calling the hybrid zoo. And I’m going to talk about several types of hybrid zoos. And I’ll end with some more far-out ideas for future zoos – looking much deeper into the future with some exciting (some might say crazy) future possibilities.
(Slide 3) So - When we think about what zoos will look like in the future, we should probably start w/ the question – will we even have zoos in the future? Some people believe that zoos will completely die out – that ethical concerns with keeping individual animals in captivity will completely trump all other concerns, including other moral quandaries related to protecting the animal species as a whole.
I disagree with these people.
In the 21st century, wild animal populations are going to be subjected to almost unimaginable challenges and crises brought about my massive human changes to the environments in which they live. Zoos will continue to exist – not just as places of recreation or entertainment or even to draw attention to these issues – they will exist as a moral imperative and as a last refuge for animals against the growing storm.
(Slide 4) But we all know zoos are not just for animals. They have always been and will always be about people too. In the 21st century – people are going to need zoos too. Maybe not as much as the animal species who are dependent on them for their very survival, but we’re going to need zoos. I’ve been interested in this issue of nature-deficit disorder for along time – and if you haven’t read this book (pub. 2005), you should. It’s about the issue of how our kids are losing access to nature in an increasingly urbanized, impoverished and technology-dependent world. It’s about the need to get everyone, kids especially, back out into nature, into the woods, etc. It’s based on the concept of biophilia. Zoos are uniquely positioned to fill this void and to give us more opportunities to interact with nature in a positive way. But enough of the sad stuff. I’m not here today to talk about these issues. What I want to talk about is what zoos are going to look like in the future.
(Slide 5) Today, we have a wealth of different wildlife institutions, devoted to the care and management of wild animal collections and populations. Today’s accredited zoos balance four (sometimes competing) goals of recreation, education, conservation, and research. These different institutions are distinguished from one another by their focus, their draw, their size, and their mission statement. One might be a small owl sanctuary near your neighborhood – another is a sprawling wildlife reserve that spans three countries. So, as you can see, we already have a lot of different types of “zoos” – and I’m defining “zoo” rather broadly.
(Slide 6) So what is a zoo?
We all think we know what they are – they’re these urban parks (usually one per city), they’re flat and horizontal, they’re mostly outdoors, where we keep different animal collections on display. On a nice day, when the weather is nice, you bring your kids in the stroller for the afternoon as a leisurely outing. Sometimes you grab lunch there. Usually it’s a quick drive – maybe a half hour or less. And you’re always home by dinnertime. You never go to other zoos besides your home city zoo, because why should you? They all have the same animals, and they all look the same – right? WRONG. What I hope to do today is to talk about some different types of zoos than what we think of as the “normal” zoo. What are some of the future directions we might be heading in?
(Slide 7) But before I talk about future zoos, we have to take a quick trip to the past. After the first couple of slides, you’re probably thinking I’m very pessimistic about the future of our zoos. But I’m not! In fact, I’m extraordinarily optimistic about the future of zoos, and I’m really excited about where we’re going. Because I can see just how far we’ve come in the past hundred years –Today’s zoos evolved from royal collections, menageries and circuses. Animals were displayed by themselves in small bare cages, with no thought of animal welfare and no understanding of how to properly care for the strange and exotic animals in the collection. Recreation, status, and economics were the only concerns. Education, conservation, and animal welfare were not concerns of these prototype zoos. So imagine just how far we’ve come in a little over a hundred years. I’m sure the next hundred years of zoo evolution will be even more amazing.
(Slide 8) Here’s some thinking on the evolution of zoos, from George Rabb – former head of the Brookfield Zoo. This diagram is from 1992, regarding the future of zoos. It anticipated a much greater focus on conservation. In a lot of ways, we’re already here, at least in the U.S. Just about every AZA accredited zoo has a primary focus on conservation, ecosystems, biodiversity, in-situ research, and more.
So where are we going from here? What happens when we extend that line further into the future?Some caveats:
This implies a linear evolution of zoos.
That zoos all started from the same place, and future zoos are all headed in the same direction along a singular line of evolution.
(Slide 9) But we all know evolution is usually diagrammed as a tree – the evolutionary tree of life. (Plus I’m a landscape designer – I have to use the tree analogy).
I see future zoo types as branching out from what has come before, in more and more different types, in a constant pattern of growth and evolution and splitting apart and forming new types we haven’t even begun to imagine. Some of these branches will intermingle with other branches and other types of institutions, forming new hybrid institutional forms. In fact, I believe this hybrid zoo is going to be a major trend over the next 50 years.
(Slide 10) So what do I mean by a hybrid zoo? We tend to think of types and categories of wildlife institutions as separate boxes, with no overlap. A wildlife rehabilitation center is completely distinct from an animal theme park, and so on. But the reality is that the distinctions between them are not so clear, and they will become more alike as we move forward. That’s what I’m calling the hybrid zoo.
(Slide 11) Here are some examples of these blurred boundaries.
Moving farther into 21st century zoo design, these boundaries will blur even further. The future zoo will occupy the middle ground – this gradient of green between a more naturalistic side and a more human-centered artificial side. These relationships do not have to be opposing dichotomies but rather rich interplays.
(Slide 12) Here’s an example. Right now, in St. Louis, if you want to see art, you go to the art museum. If you want to learn about history – the history museum. You want science at the history museum? Too bad! You want gardens at the zoo? Well, you might be in luck. After all, the full historical name is “zoological park.” And we’re starting to see science displays creep into zoos. And more and more art is making its way to zoos as well.
So why do these have to be separate institutions? Why can’t we have one hybrid institution, where you can go and see animals and art, and learn some science and history, and have fun all the while doing it? What sort of zoo would that be?
(Slide 13) Well, it might look something like this: our own City Museum. This is a highly interactive, multi-story, zoo-like museum that combines animals with art, history, science, and play. It’s a tactile and sensory rich experience, in which visitors can scramble through underground chambers like burrowing prairie dogs, or climb into a lofty nest high in the trees, or playfully splash in a river grotto. Where they can physically be the animals they have come to see – the modern explorer and adventurer in an urban wilderness of visual and tactile richness. Opportunities for a multifaceted cultural experience, with an emphasis on rotating exhibitions and freeform visitor activities. Opportunity to repurpose un-used urban buildings.
(Slide 14) Here’s another example: COSI = Center of Science and Industry. Science museum on Scioto riverfront in downtown Columbus Ohio – opened here in 1999, institution since 1964. Really cool Ocean zone: Poseidon themed interactive water play area, where we learn about things like laminar flow and water surface tensions, while having fun soaking our friends in the process. Why is there not an aquarium here? This is the perfect place for it.
(Slide 15) Here is the next hybrid zoo type: this is what we do here at PGAV so I’m not going to go into much detail. Suffice it to say – the hybrid zoo/theme park has been around for awhile, but the trend is becoming bigger and bigger as we move into the future, and in fact it is one of the primary branches for the future of zoo evolution. In the future, the primary focus of such theme parks will still be on recreation and entertainment, and they will continue to lead the way in creating great visitor experiences and great storytelling. But the theme parks will draw more and more from other zoos and wildlife institutions. Conservation, education and even research will likely be a greater part of the institutions’ (and the public’s) focus in the future. There will be more sharing – and more blurring - between theme parks and other zoo institutions.
(Slide 16) Here’s another hybrid type. This is a map of Columbus OH, showing the Zoo (the orange circle) as well as several parks and urban greenways. Urban zoos are going to become decentralized and modeled on the university concept with multiple regional campuses scattered throughout the city and region. Merge with other urban greenspaces: metro parks, green trails, city parks and regional urban greenways. Oases throughout the city - a small aquarium here, a monkey island there. Multitude of smaller environments to maintain an educational and recreational access to the wild and to nature. The urban zoo will become more accessible, from both a physical and economic standpoint. More emphasis on local wildlife. Opportunities for nature recreation: ziplining, kayaking, ropes courses, bicycling, etc.
(Slide 17) Here’s another, a relatively new kind of zoo that we’re going to see a lot more of in the future: the safari park. A sprawling, regional destination – a hybrid between a standard zoo and a large wildlife preserve, usually housing African safari-type animals. Adventure park and destination, a full-day and possibly multi-day trip. 1,800 acre zoo visited by 2 million people annually, houses over 2,600 animals representing more than 300 species, as well as 3,500 plant species. Lots of different animal tour and recreational opportunities: caravan safaris to giraffe and rhino exhibits, behind the scenes safaris, cheetah runs, ropes courses, zip lines.
(Slide 18) Another example: the Wilds. 9,154 acres (37.04 km²) of reclaimed coal mine land. The Wilds is the largest wildlife conservation center for endangered species in North America. Home to over 25 non-native and hundreds of native species, including Scimitar-Horned Oryx, Przewalski's Horses, and Hartmann's Mountain Zebras. Private, non-profit - The International Center for the Preservation of Wild Animals, Inc. (ICPWA)– now working in partnership with the Columbus Zoo open between the months of May and October.
(Slide 19) Safari parks are destined to be huge regional draws with the potential for overnight/multi-day stays. Potential for ecotourism and “glamping” – in a yurt. San Diego Safari Park has the “Roar and Snore Safari” where you spend the night in an upscale tent (upper left). The Wilds has the yurts at Nomad Ridge (photos on right). Varying levels of luxury and ruggedness – I’d rather sleep in the fancy yurt in the center instead of that open air birds nest.
(Slide 20) When we think of national park wildlife, we think of the animals as being completely wild. These wildlife encounters, usually from our vehicles, are seen as a completely wild encounter with unadulterated nature. We believe that this is the “real deal”. We never really think of animals in the national parks or wildlife reserves as anything but completely wild. But the truth is, there really is no such thing as true, untouched “wilderness” anymore.
(Slide 21) The animals in national parks are (for the most part) free-ranging, but they are still intensely and actively managed. This happens in not just the North American parks but also those in Africa. Examples:
At Rocky Mountain National Park, rangers manage elk herd sizes through a variety of birth control techniques
There are concerns at Kruger National Park in South Africa, where there are now arguably too many elephants that are destroying most of the vegetation.
National parks are really not so different from zoos
More and more control measures are being instituted (bear-proof food lockers, etc.)
Much of the park rangers’ time is spent monitoring the animals, relocating nuisance individuals when necessary, tracking the size and health of herd populations, eradicating invasive and exotic animal species, and more
Future for these parks - even more wildlife management to protect the animal populations; more borrowing and sharing of ideas with zoos and other wildlife institutions.
(Slide 22) Final hybrid type. For much of their history, many wildlife rehabilitation centers refused to accommodate visitors. These are places that nurse sick, injured or orphaned wildlife back to health, for release back into the wild. They have seen visitors as nuisances or distractions at best or, at worst, as people in direct opposition to their stated goals. Some have associated visitor accommodation with the “lesser” goals of recreation and entertainment. But that has been changing. These places are realizing that their facilities are unique places for visitor education and awareness, and are really starting to attract visitors with interpretive experiences and elaborate visitor facilities. They will continue to merge with other types of zoos as we move forward.
(Slide 23) Ok, that was a quick overview of several different types of hybrid zoos. Now I’m moving on to other directions: Looking further into the future, many of these trends are for zoos 50 to 100 years from now.
(Slide 24) First Trend: the Bubble Ecology Zoo – a self-contained place that replicates full ecological systems and habitats, in order to best house animal species outside of their preferred/original climatic and bioregional zone. Inspired by the ideas of Buckminster Fuller. We are already starting to do this, but this is taking it one step further to create a fully-functioning self-contained ecosystem. Designed by an associate of Buckminster Fuller. Still world’s largest closed system. Now owned by the University of Arizona since 2011. 3.14-acre structure. Generally considered to be an unmitigated disaster (from the perspective of a social experiment), but is still inspiring future zoos.
Info from web: “Constructed between 1987 and 1991, it explored the web of interactions within life systems in a structure with five areas based on biomes, and an agricultural area and human living and working space to study the interactions between humans, farming and technology with the rest of nature. It also explored the use of closed biospheres in space colonization, and allowed the study and manipulation of a biosphere without harming Earth's.”
(Slide 25) Houses plants collected from all around the world. Opened in 2001. Info from Web:
The domes consist of hundreds of hexagonal and pentagonal, inflated, plastic cells supported by steel frames. The first dome emulates a tropical environment, and the second a Mediterranean environment.
The Tropical Biome, covers 3.9 acres and measures 180 ft high, 328 ft wide and 656 ft long. It is used for tropical plants, such as fruiting banana trees, coffee, rubber and giant bamboo, and is kept at a tropical temperature and moisture level.
The Mediterranean Biome covers 1.6 acres and measures 115 ft high, 213 ft wide and 443 ft long. It houses familiar warm temperate and arid plants such as olives and grape vines and various sculptures.
Meandering path with views of the two biomes, planted landscapes, including vegetable gardens, and sculptures that include a giant bee and towering robot created from old electrical appliances
(Slide 26) Info from Web:
"Desert Dome" is the world's largest indoor desert, as well as the largest glazed geodesic dome in the world. Opened 2002. Beneath the Desert Dome is the Kingdoms of the Night,and both levels make up a combined total of 84,000 square feet. The Desert Dome has geologic features from deserts around the world: Namib Desert of southern Africa; Red Center of Australia; and the Sonoran Desert of the southwest United States.
Lied Jungle is one of the world's largest indoor rainforests: Visitors can walk along a dirt trail on the floor of the jungle as well as on a walkway around and above the animals. Opened 1992. 123,000 square feet of floor space, of which 61,000 square feet is planted exhibit space; 35,000 square feet of display management area; and 11,000 square feet of education area
(Slide 27) Designed unveiled in 2010, but plans shelved in 2011 due to loss of funding. Also included plans for a hotel. Info from web:
112 feet high and larger than the Tropical House at Eden. The project covers 172,000 square feet and will simulate the natural African rain forest habitats of the Congo. It includes an undulating dome which will be one of the largest ETFE clad free form roof structures in the world and contain a jungle canopy with an authentic climate.
The 'Heart of Africa' Biodome will be home to a band of gorillas, a large troop of chimpanzees, okapi (rare giraffe-like creatures), birds, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and invertebrates.
An interactive water ride will provide extensive views of the animal enclosures.
Themed retail and dining facilities will also be incorporated.
(Slide 28) Architectural Design Competition for a Tropical Garden. Unbuilt, designed in 2011
(Slide 29) Designed in 2009. Four biozones: Central Asian Steppe, Arctic Pole, Asian Temperate Forest, Central Asian Mountain. Info from web:
“The architects conceived an intelligent rehabilitation of the zoological island of Korkeassari from the circulation in the different biozones to the construction of a contemporary entrance edifice. Here the architecture disappears in favor of controlled geography.”
Described by architects:
“The zoological island of Korkeasaari will be cut off again. Its architectural interventions will be concentrated to make it wild and mysterious once more – a park / garden as a place of popular privilege, the nobility of the future city.
Architecture disappears in favour of controlled geography, like the resurgence of a neighboring landscape. The entrance grouping the set of utilities crucial to the running of the zoo becomes a focus of visual identity, somewhere between form and shapelessness, pierced with cavities.
Like layers of skin peeled back to receive an implant, there will be an above and a below that dialogue and interpenetrate one another. Areas of light, uncertainty, reflections and depths will be developed, offering the first emotions of a visit that will play on time and the seasons through four biozones :
Central Asian Steppe
Arctic Pole
Asian Temperate Forest
Central Asian Mountain”
(Slide 30) Multistory zoo. Why not go vertical? Especially in increasingly urbanized and dense populated areas. Zoos don’t have to be horizontal. Aquariums have been going vertical for decades.
Dutch Pavilion: explored topics of ecology, congestion, population density, the relationship between natural and artificial
6 levels: dune landscape, greenhouse landscape, pot landscape (which has trees), rain landscape, and more
Info from web:
“The idea of the pavilion was characterized by the superimposition of six ways of being of the landscape.From the ground floor, the "dune landscape" leading to "greenhouse landscape," space in which nature and, above all, agricultural production, showed strong union with life, even in the new high tech world.In the "pot landscape" big pots hosting the roots of trees located on the top floor, while throwing screens and digital images of light and color messages.
"Rain landscape was changing in the space devoted to water, which was turned into a screen and in support of audiovisual messages; large trunks of trees populated the" forest landscape" while building on top of the" polder landscape "hosted large wind blades and a large green area.”
(Slide 31) Star-shaped tower based on a nucleus of a tree trunk, designed to maximize space, views, and circulation. Sustainable strategies: rainwater harvesting, solar power. Info from Web:
“The Vertical Zoo is a balanced and sustainable space where people and animals can coexist in harmony. Wrapped in lush vegetation, the star-shaped building makes use of green building strategies to reduce heat gain, encourage natural ventilation and soak up rainwater. Totally self-sufficient, the tower's aim is to be a sustainable refuge for all animal kingdom species.
Built from a six armed star-shaped level designed to maximize space, views and circulation. It is based on a nucleus or a tree trunk from which emerges six branches, each 20 sq meters in size which all serve different programmatic needs. These program blocks provide space for zoo activities, visitor needs, administration, circulation and ventilation, and spaces for sustainability. Modular by design, more star-shaped levels can be added on top as needed or as funding becomes available for new facilities.
Capable of providing its own water and energy through rainwater collection and solar power. Arrangement of the star-shaped levels encourages natural ventilation and improves views. Multiple towers can be built together to create a larger interconnected complex.
The Vertical Zoo is designed to be as much about the animals as it is about the people who visit and encourages meeting and cohabitation as a way to promote equanimity between the species.”
(Slide 32) A competition for the Costanera Sur Ecological Reserve. Info from web:
A towering habitat meant to resemble a natural cliff that would also provide nesting ground for migratory birds
Goal: recreate a cliff habitat for the types of animals that would naturally be living in such an environment
Footpath winding around an inner core of animal enclosures, all within a net-like steel shell that lets in air and sunlight as well as a controlled amount of rainwater in certain areas. The nets and cables support vegetation that gives the tower a more natural feel, and select pockets serve as open-air nesting for the birds.
Visitors reach the tower in cable cars connected to the public transportation system, and can then take in an even more spectacular view on a high-level observation deck.
(Slide 33) Low-impact zoo: a Zero Energy Zoological Island in South Korea. Sustainable strategies: zero-carbon transport systems, renewable energy sources, rainwater collection sites, and all waste would be reused as either composted fertilizer or biofuel. Roughly dodecahedron-shaped habitat tower. Info from web:
“The zoo’s landscape of natural peaks and valleys is ideal for zoo development. The flat valleys could host animals, while more mountainous areas could be protected and treated as nature reserves. All transportation, energy sources and building systems would be housed in a so-called “infrastructural green belt” located at a height of 20 meters. Everything above and below would remain untouched.”
(Slide 34) A wildlife corridor is an area of habitat connecting wildlife populations separated by human activities or structures (such as roads, development, or logging). Huge, regional scale – possibly spanning multiple countries. Allows an exchange of individuals between populations. This may potentially moderate some of the worst effects of habitat fragmentation,wherein urbanization can split up habitat areas, causing animals to lose both their natural habitat and the ability to move between regions to use all of the resources they need to survive. Habitat fragmentation due to human development is an ever-increasing threat to biodiversity, and habitat corridors are a possible mitigation. Here are some examples of wildlife bridges, which allow animals to cross human structures unimpeded. Especially useful for wide-ranging animals like wolves (Though, if I’m a wolf, I’m hanging out right by the wildlife bridge for prey).
(Slide 35) Here’s another example: green roofs. Becoming increasingly common. Scattered throughout dense urban areas on multiple rooftops. These could become home to migrating bird species and other migrating animal populations.
(Slide 36) Virtual or digital zoo is a way to interact with animals remotely, using technology. We all remember the PandaCam Crisis of 2013, also known as the government shut-down, when the Smithsonian’s National Zoo live feed from the panda exhibit went dark. As new technologies emerge, there will be more and more opportunities to view and interact with animals all around the world. The world is shrinking. To be honest, I find this type of zoo much less compelling. There is NO substitute for real, live, face-to-face interaction with real animals.
(Slide 37) In all likelihood we will have the technology to bring back extinct animal species in the next century. Advances in cloning technology and genome mapping. Likely species include:
Wooly mammoths, dodo birds, passenger pigeons, a relative of the zebra called the quagga, and the so-called "Tasmanian wolf," (which died out in the 1930s, according to Michael Noonan, a biologist at Canisius)
Not dinosaurs – we’re not making Jurassic Park
There are obvious, enormous ethical issues with this, but I’m not going to open that can of worms today.
(Slide 38) What I will say is this: This is probably going to happen in the next centuryso we should probably be thinking about what that means.
What does this mean for future zoos? Will these be the new pandas? The superstar species that draws most of the visitors?
If offered a live mastodon, what zoo will turn them away?
How do we keep these species from becoming just a mere curiosity?
How will we know if their physical, environmental, social and intellectual needs are being met?
Shouldn’t the ultimate goal be reintroduction to the wild rather than keeping a captive population?
It’s certainly a complicated issue, but a very real possibility.
(Slide 39) We’ve been sending animals (specifically mammals)up into space since the late 1940s. Lots of primates through the 1950s and 1960s. Even today, experiments with fish, mice, and more on the International Space Station. Primarily for research purposes thus far. What happens when we start to colonize space?
(Slide 40) Eventually we’re going to start colonizing space – the moon, Mars, an asteroid, the moon Europa, or elsewhere in the solar system. When we think of space colonies, we tend to think they will look something like this: Barren, dull, lots of metal and hard surfaces; The only life forms are human.
(Slide 41) But I think future space colonies will eventually look something more like this: with simulated natural habitats and lots of different life forms. Stanford Torus: 1975 proposed designfor a space habitat capable of housing 10,000 to 140,000 permanent residents. Info from web:
Ring-shaped rotating space station
Interior space of the torus itself is used as living space, and is large enough that a "natural" environment can be simulated; the torus appears similar to a long, narrow, straight glacial valley whose ends curve upward and eventually meet overhead to form a complete circle. The population density is similar to a dense suburb, with part of the ring dedicated to agriculture and part to housing
(Slide 42) Here are some other views. Whether we start colonizing the final frontier on giant rotating torus-shaped stations, or on terraformed colonies on the moon, Mars or Europa – we will bring our animal cousins with us.
(Slide 43) Conclusion:
While we don’t know all of the forms that zoos will take in the future
We do know that there will be lots of new types of zoos
We also know that the boundaries will blur between zoos and other institutions, creating fascinating new hybrid typologies
There are lots of exciting new frontiers to explore
As Zoo designers, we have the power to shape this new world and I’m really excited to keep moving forward
(Slides 44 & 45) Resources and Links

By Trisha Crowe A moment of silence for Marius the giraffe, and then…..What?
Boycott the Copenhagen Zoo?
Boycott ALL zoos?
I say let’s rally around something we can agree upon….that the mistreatment or exploitation of any species is not ok. The difficult thing is that how each person defines these terms is a highly personal decision. It is based on the innumerable messages we get as we grow up about what is right and wrong, what is fair and unfair, and how we either feel or are taught about other living organisms.
As a self-professed animal lover I personally was stunned to see Marius’s story in the headlines. Regardless of where you stand on the spectrum of “animals are just like humans”, vs. “animals are here only to serve us”, I think we can agree that most of us do not want to see a healthy two year old giraffe killed and then publicly skinned and fed to lions. In our cultural views the Copenhagen Zoo’s handling of this issue has been an abomination, no doubt. But now what?
Based on reaction I have seen online, many people are ready to reject zoos altogether. I can understand this sentiment because there was a period in my life when I decided that I did not want to go to zoos anymore. Instead of feeling happy, uplifted or educated it seemed like I always left zoos feeling sad for the confined animals (from this point I will use “animals” loosely to represent all zoo and aquaria species). I thought the enclosures were mostly too small and too sparse, there weren’t enough enrichment opportunities for animals to play or exhibit natural curiosities, and on top of all of that some animals didn’t even get to leave the confines of their “holding areas” (I saw these as concrete cages) very often.
Flash forward; it took me almost 10 years to realize that the decision I had made to stay away from zoos did not do one bit of good for any animal anywhere. I realized that zoos are not going away. In the United States, zoos that are accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) have higher attendance per year than all major sporting events combined. And did I really want them to go away anyhow? No, what I wanted was for them to be better. I decided that the right thing to do was not to ignore the problem, rather see what I could do to improve things. With this goal in mind I enrolled in a master’s program in landscape architecture. I did my thesis on zoo exhibit design with an eye on contributing to the design and construction of better enclosures and holding areas.
My revised attitude towards zoos has taken me a long time and has not always been easy; however since 2006 I have met with dozens of zoo and aquarium professionals who have given me a world of valuable time and a lot of insight. I have talked with keepers, horticulture staff, directors, COO’s, CFO’s, education staff, marketing staff, designers, and development and membership staff. While these people all have different educational backgrounds and varying views on animal “rights”, every single person I have met has had at least this in common – their love of wildlife and their desire to make a positive contribution to their organization and its occupants.
After having all of these conversations I realized that my past view of zoos was based on a very limited sample size and little real information. What challenges do zoos face? Why do they take the actions that they do? I really had no idea and unfortunately this made me mistakenly clump every negative act of every individual at every zoo into one category - bad.
What I have learned over the past ten years, however, is that zoo professionals are out there working hard to make positive changes. Within the past thirty years we have come a very long way. While in the 1970’s I had a lot of fun throwing marshmallows and peanuts to the elephants at my local zoo I am much happier to know that species diets have been well considered and are contributing to healthier animals. The 1980’s saw a widespread acceptance and execution of the use of more naturalistic enclosures. Enrichment opportunities – things like big blocks of ice with frozen treats inside or design elements which allow for an animal to exhibit their naturalistic behaviors – have grown into their own field of expertise. The psychological well-being of animals is now at the forefront of zoo keepers and administrator’s minds, so efforts have increased to address stress-based or “zootypic” behaviors such as animals pacing. But here’s the thing, change cannot happen overnight. And it cannot happen without passionate people letting their voices be heard.
I once felt helpless to do anything that would make any difference at all, but I eventually decided that my way to try and make a difference was to get my degree in landscape architecture and become a member of AZA. Now I am also trying to raise awareness that what zoos really need the most right now to continue their transformation into the kinds of institutions we want them to be is our support.
Regardless of your current impression of zoos they are a valuable resource and carry valuable messages to the public. They connect humans to wildlife in an up-close and personal way not otherwise possible. With increasingly dynamic education they foster participation in global environmental initiatives and help create a public concerned about the future of our planet, and wide-ranging conservation programs aim to preserve a vast variety of species in their natural areas. Zoos and aquariums are some of the only places left where a kid would rather look at what is in front of them than what is on their phone or computer screen.
So today I implore you, don’t dismiss all institutions. Become a member at an AZA-accredited zoo you have confidence in to show your support. Volunteer at your local zoo or aquarium. Write a letter when you are bothered by things you see. Get involved with a wildlife conservation initiative that you believe in. In the case of Marius the giraffe, write the Copenhagen Zoo an email voicing your concern.
Change cannot happen without us.
Trisha Crowe has been a team member in Pittsburgh, PA-area businesses focusing on design, planning and environmental issues for over 10 years. Trisha’s passion - and primary reason for completing her Master's of Landscape Architecture in 2010 - is zoo exhibit design.

Check out my latest article on PGAV Destinations Blog.

The following is an adaptation of a presentation I gave in September 2013 at the AZA National Conference as part of the session ‘Enrichment as Guest Experience.’ This is part two of two. Check out Part 1 here. What is experience?
Put quite simply, it’s everything. Literally and figuratively.
Experience at zoos and aquariums is everything from the moment your guest turns onto your property in their car. It’s every moment, every interaction with staff or animals, every view.
All of these moments combine and culminate to create an ultimately positive or negative association with your institution.
Experience is also quite possibly the most important aspect of what you do.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs summarizes the pattern of human motivations from the most basic to the sublime. A parallel can be made to your guests’ needs. Meaning, before we can reach people on a transformational level, we must satisfy their lesser needs beginning with the desire first to be comfortable and safe, moving through to simply having a good time, onto learning something, which sparks something deeper (the ‘I wanna help’ moment), and ultimately providing them the inspiration to take action.
The key here is to remember that your guests do not come through the door ready to be transformed. We must provide a great guest experience starting with the most basic needs guiding them to transformation.
Why do we care?

This one’s simple. The ultimate goal of every visit is to create or facilitate transformational experiences. We do this through engagement, empathy and empowerment. We aim to create Activists—both for conservation and wildlife, but also for your institution itself. Your guests are your best marketing tool and PR managers—when they’re on your side.
How do we optimize experience to achieve our goals?
One major method is through the use of storytelling. Yes, it’s a buzzword right now, but for good reason: it works. Human beings have been using storytelling as a means to convey information for thousands of years. Why not use what works? And it’s universal, appealing to every age group, ethnicity and educational background on the planet.
But stories are no longer passive or 2D experiences. Our lives are dominated by choice and interactivity. We live in an instant gratification society. This doesn’t necessarily mean that every experience should incorporate digital media. It simply means people today like to display some control over their environment, and the more choice we can give them, the more engaged our guests will become.
Storytelling in zoos primarily occurs through three methods:
1. Environment: Sensorial cues begin to tell a story by creating a setting
Humans are highly visual, and in fact, as state before, we’re highly sensorial—and the connection with the senses, the more powerful memories may be. Creating places that stimulate the senses triggers other memories and sparks the imagination.
Environment can also contribute to story with the use of the unexpected. Our minds work by piecing information together by making assumptions based on past experiences. When something doesn’t look or feel as we expected, our minds go into overtime trying to reconcile the past experience with the current. This leads to a simple truth: surprise gets our attention.
2. People: Direct and effective communication of story
Humans are social animals. We yearn to connect with others. We want to find commonalities, to empathize. So it’s no surprise that storytelling is most effectively achieved by people connecting with people. In fact, it’s been shown in study after study that guests learn more and are more interested in the animals at zoos after interacting with docents and keepers.
3. Animals: The heart of the story
The best animal stories are those told by the animals themselves. Similar to our desire to connect socially with other humans, we also want to connect with animals. And if you examine how we connect, you’ll see it’s often with our senses—perhaps most importantly, through the sense of touch.
One of the most memorable, most affecting guest experiences is being able to physically touch animals. But, if we cannot touch, we want to be as close to the animal as possible. We want to interact with the animal, we want to get a reaction from the animal. We want to feel as if we’ve been noticed and seen—like we’ve engaged directly—with the animal. Just like how we connect with people.
And again, just like how we connect with each other, we’re seeking to find similarities with animals; looking for comparisons between how we look and behave. The stories we tell about animals are often most engaging when we’re building empathy through understanding—by looking for ways that they’re ‘just like me!’
These three elements of storytelling are also major aspects of Enrichment. Environment is enrichment through provision of choice, change in habitat, toys, etc. People deliver the enrichment whether through keepers or even special guest experiences. And, of course, the Animals are the recipients of the enrichment.
Getting creative about how we enrich the animals in captivity while also keeping the guest experience top of mine will only continue to improve the guest experience and ability of zoos and aquariums to achieve their missions.
The following is an adaptation of a presentation I gave in September 2013 at the AZA National Conference as part of the session ‘Enrichment as Guest Experience.’ This is part one of two.
The guest experience is a critical component to any institution that aspires to educate the general public in a single visit. Zoos and aquariums have a trick up their sleeve, however: the animals. And as long as we optimize the connection between guests and the animals, the guest experience is elevated. In order to ‘optimize connection,’ zoos and aquariums can and should use enrichment as a critical element of the guest experience.
Zoos and aquariums are doing fantastic work across the country and around the world working on conservation, research and education programs.
With all of this great work, sometimes a critical characteristic of the institutions is overlooked: the Guests. Zoos and aquariums are places for leisure and recreation.
They are places that people primarily visit for wholesome, family fun which means we have a captive audience, day in and day out, to which we can directly connect. Because of that, we cannot overlook the fundamental aspect that keeps people coming back again and again…The Guest Experience.
Simply put, if guests don’t have a great time, they simply won’t come back.
What goes hand in hand with having a great time? Creating memories. We have to always remember that we are helping our guests make lifelong memories.
Indulge me here. Let’s take a moment to explore memory making. Positive or negative, memories capture a moment in time, and influence future decision making. A memory is truly a living portrait of an experience--and an experience that makes the most powerful memory has some very specific attributes.
There’s a touch, taste, smell, sound or sight associated with the experience. Something that will bring you back to that moment in an instant. For me, mothballs remind me of Spring Break at my grandma’s in Florida—doing homework at the kitchen table from the extra days off for the trip. For some people, music is especially nostalgic…Weezer’s Undone (The Sweater Song) takes me back to dancing around my high school best friend’s living room.
Happiness, love, fear, embarrassment are captured fully in memories. Our happiest moments are easily remembered, of course. But, on the flipside, trauma also sticks with us. One of my earliest memories is of Santa—and of me, at 3 or 4 years old, hiding under the dining room table at my grandparents’ house clutching the table leg for dear life, tears streaming down my face, shaking in fear of the gigantic, loud, creepy stranger with a weird laugh sitting in my Pappy’s chair and eating our cookies. Not cool, Santa. Not cool.
Our first time. It sticks with us. The experience of trying and failing, trying and overcoming. The excitement of doing something for the very first time. These are strong experiences that beget strong memories. Even for seasoned professionals, that first snuggle with a snow leopard cub sticks with you.
Okay, so we get memory making in general, so next we'll talk about memory making—and thus experience--at zoos and aquariums specifically. Check back soon for Part II.
You want a little insight into me? Check out my latest Blooloop.com rant about the inaccuracy and overuse of the word 'wild'. It's controversial. I promise.